How To Calculate Kcat
How To Calculate Kcat. Example of km and kcat from educator.com’s biochemistry class. Vmax is equal to the product of the catalyst rate constant (kcat) and the concentration of the enzyme.
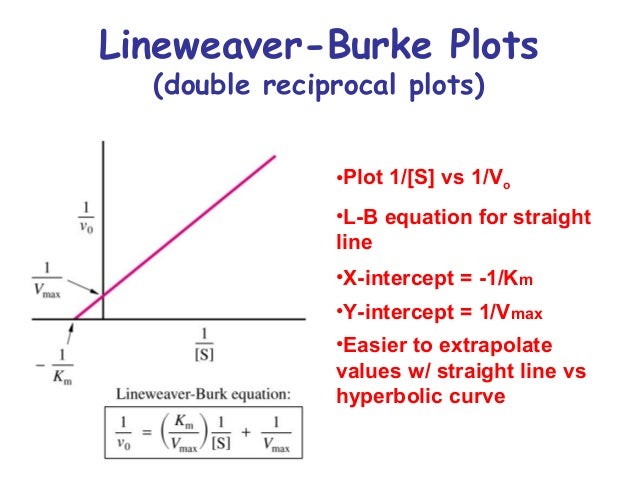
In this case you would find the km from the plot, get the vmax from the plot as well and divide it by [e] to get kcat. Then simply kcat/km for the cat efficiency. How to calculate kcat from vmax?
From The Welcome Dialog, Choose Xy And Choose To Use The Michaelis Menton Sample Data.
Kcat is equal to k2, and it measures the number of substrate molecules turned over by enzyme per second. The michaelis constant (k m) is equal to the substrate concentration. How do you calculate kcat?
In This Case You Would Find The Km From The Plot, Get The Vmax From The Plot As Well And Divide It By [E] To Get Kcat.
Edited july 20, 2015 by gnothiseauton Michaelis menten equation is used for determining rates of enzyme controlled reactions. Then simply kcat/km for the cat efficiency.
To Calculate Kcat, Scientists First Mix Several Test Tubes With Varying Concentrations Of Substrate (Known As An Enzymatic Assay) And Test Them At Constant Time Intervals With A Light Spectrophotometer To Measure The Growing Concentrations Of Product Molecules.
When you calculate kcat , you can also write. Kcat is equal to k2, and it measures the number of substrate molecules turned over by enzyme per. Kcat km =k1 k2 k−1 k2 k 1 is the on rate for binding.
The Unit Of Kcat Is In 1/Sec.
Example of km and kcat from educator.com’s biochemistry class. How to calculate kcat from vmax? Kcat is equal to k2, and it measures the number of substrate molecules “turned over” by enzyme per second.
Kcat Represents Maximum Number Of Substrate Molecules Which Enzyme Can Turn Into Product.
How do you calculate kcat km? The unit of kcat is in 1/sec. Several determinations of a quantity can be made using the same apparatus, with differing results.
Post a Comment for "How To Calculate Kcat"